Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and the development of new and effective therapies is crucial in the fight against this disease. One promising area of research is the use of small molecule inhibitors, such as TPCA-1, as a potential treatment for cancer. TPCA-1 is a small molecule that has been shown to have anti-cancer activity in preclinical studies, and its ability to target multiple pathways in cancer cells makes it a multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy.
What is TPCA-1
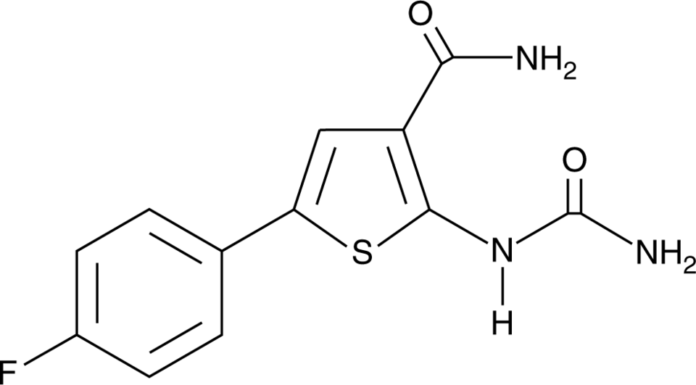
TPCA-1 is a small molecule inhibitor that has been researched extensively in recent years for its potential applications in scientific research. Small molecule inhibitors, like TPCA-1, are a class of drugs that work by binding to and inhibiting the activity of specific target proteins in the body. These molecules are typically smaller in size than traditional biologic drugs, such as antibodies, and can be designed to target specific proteins that are involved in disease processes.
One of the unique features of TPCA-1 is its ability to target multiple pathways in cancer cells, making it a multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy. This allows TPCA-1 to potentially overcome drug resistance, a major challenge in cancer treatment, and provide a more effective treatment option.
In addition to its anti-cancer activity, TPCA-1 has also been shown to enhance the efficacy of other cancer therapies, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy, making it an attractive option for combination therapy. TPCA-1 has also been shown to be safe and well-tolerated in preclinical studies, which is an important aspect for the development of new cancer therapies.
Targeting The Oncogenic Protein STAT3
One of the main targets of TPCA-1 is the oncogenic protein, STAT3. This protein is commonly activated in cancer cells and plays a critical role in cell proliferation, survival, and drug resistance. TPCA-1 has been shown to inhibit the activity of STAT3, leading to the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. This mechanism of action makes TPCA-1 a potential treatment option for cancer types where STAT3 is commonly activated, such as breast, lung, and gastric cancer.
Multi-targeted Approach of TPCA-1
In addition to targeting STAT3, TPCA-1 has also been shown to target other signaling pathways in cancer cells. For example, TPCA-1 has been shown to inhibit the activity of the PI3K/Akt pathway, a signaling pathway that is often activated in cancer cells and plays a role in cell survival and drug resistance. TPCA-1 has also been shown to inhibit the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, another signaling pathway that is commonly activated in cancer cells and plays a role in cell proliferation and survival. The ability of TPCA-1 to target multiple pathways in cancer cells makes it a multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy, potentially overcoming drug resistance and providing a more effective treatment option.
TPCA-1 Enhancing the Efficacy of Other Cancer Therapies
The ability of TPCA-1 to target multiple pathways in cancer cells has also been shown to enhance the efficacy of radiation therapy. TPCA-1 has been shown to sensitize cancer cells to radiation, leading to an increased response to radiation therapy. This suggests that TPCA-1 could be used in combination with radiation therapy to enhance the treatment effect. TPCA-1 has also been shown to have a synergistic effect when used in combination with other cancer therapies, such as chemotherapy. For example, TPCA-1 has been shown to enhance the efficacy of the chemotherapy drug, cisplatin, in preclinical studies. This suggests that TPCA-1 could be used in combination with chemotherapy to enhance the treatment effect. The ability to enhance the efficacy of other cancer therapies by targeting multiple pathways in cancer cells makes TPCA-1 an attractive option for combination therapy, which has the potential to improve patient outcomes.
Safety and Tolerability of TPCA-1
Safety and tolerability are crucial for the development of new cancer therapies, and TPCA-1 has been shown to be safe and well-tolerated in preclinical studies. These studies have shown that TPCA-1 has a low toxicity profile and does not have significant side effects. This is an important aspect of TPCA-1 as a potential treatment for cancer, as it suggests that it may have a favorable safety profile in human clinical trials.
Future Directions of TPCA-1
The preclinical studies discussed in this paper demonstrate the potential of TPCA-1 as a multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy. However, the data presented here is based on in vitro and in vivo studies, and further research is needed to confirm the efficacy and safety of TPCA-1 in human clinical trials. Additionally, further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosing, schedule, and combination therapy regimens for TPCA-1.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TPCA-1 is a small molecule inhibitor that has shown anti-cancer activity in preclinical studies. Its ability to target multiple pathways in cancer cells makes it a multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy, potentially overcoming drug resistance and providing a more effective treatment option. TPCA-1 has also been shown to enhance the efficacy of radiation therapy and other cancer therapies, and to be safe and well-tolerated. Further studies are needed to confirm theefficacy and safety of TPCA-1 in human clinical trials. However, the concept of multi-targeted approach to cancer therapy using small molecule inhibitors is a valid and active area of research in the field of cancer therapeutics. Benchchem’s scientists have shown that further studies are needed to identify TPCA-1 and develop the molecule that can target multiple pathways and overcome drug resistance, ultimately leading to more effective cancer treatment options.