When building a Communication Intelligence (COMINT) system, there are many factors that need to be addressed carefully to ensure you capture and process signals effectively. My own experience with COMINT systems started as a hobby, but it quickly became clear that this is a field requiring discipline and precision. Many people might feel overwhelmed when beginning, but by breaking down each element step-by-step, the process becomes manageable and rewarding.
Key Points:
- Define the scope of your COMINT setup before selecting equipment.
- Choose appropriate hardware based on the frequencies you want to monitor.
- Configure your software to decode the necessary signals.
- Set up antennas tailored to the specific frequencies.
- Ensure proper signal processing and data storage.
- Regularly maintain and upgrade equipment for optimal performance.
1. Define Your Purpose and Scope
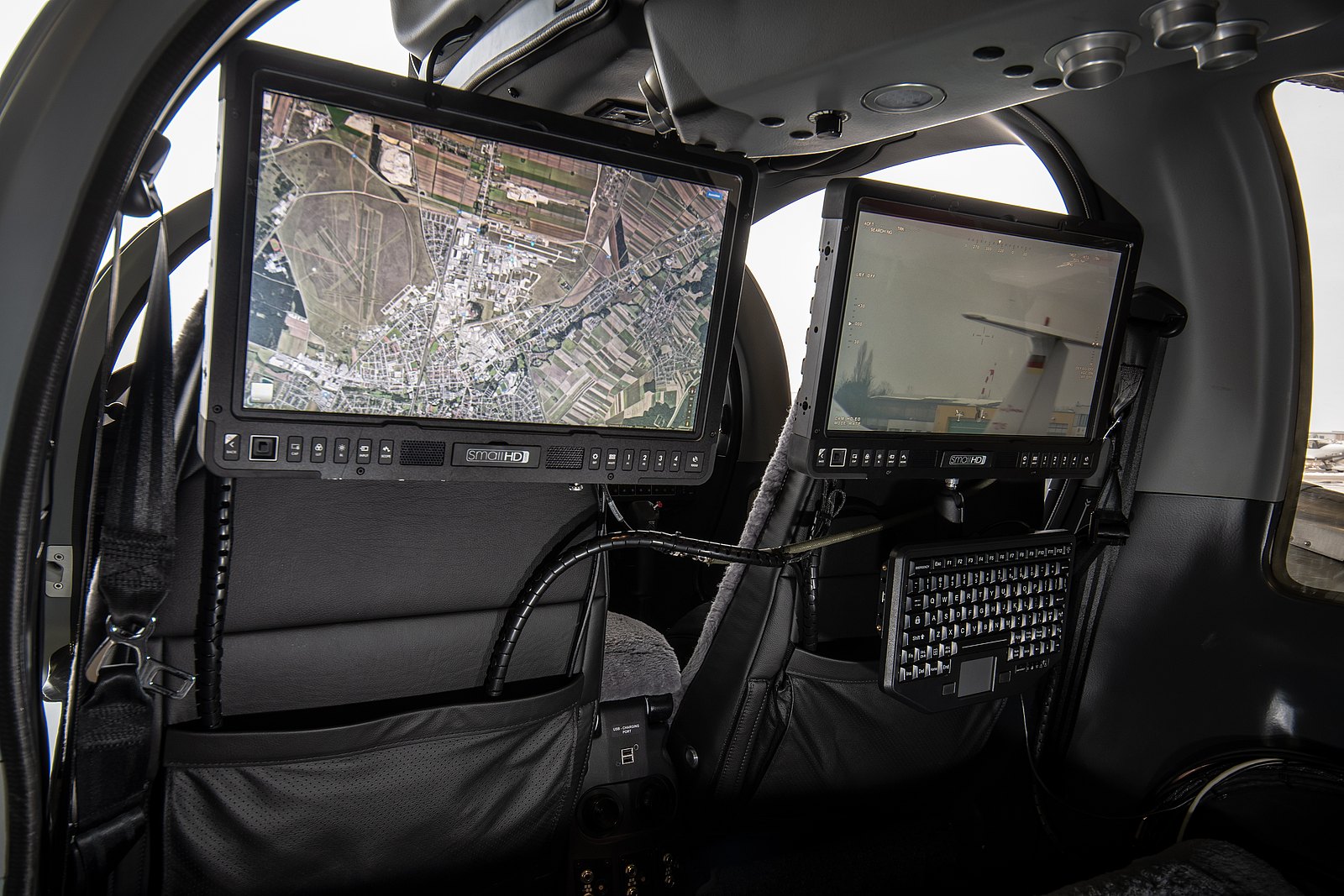

Start by identifying why you need a COMINT system and the specific signals you plan to capture. This is essential because not all systems are created equally, and the technology you select depends heavily on your objectives. For example, a military-grade system might focus on a broad range of high-frequency signals, while a civilian setup may target lower frequencies used by local communication.
To avoid overspending, carefully match your setup with your needs. For me, this involved extensive research into different hardware options. I found that most amateur setups could handle signals up to a certain range, but professionals need to consider much more robust solutions.
2. Choose the Right Hardware
Choosing the right hardware is arguably the most critical step. Depending on the frequencies you wish to monitor, you’ll need specific hardware that can capture and process those signals. A base station and signal decoders are non-negotiable. You will also require a powerful receiver capable of monitoring a wide range of signals.
If you’re new to COMINT systems, consider starting with the basics—then, as your needs grow, you can upgrade. When I upgraded my own setup, I discovered that selecting a receiver compatible with ELF-HF signals was essential, especially when decoding signals. One of the best tools for narrowband signal analysis is the Krypto500 software, which works seamlessly with any COMINT system. This software supports signal decoding for a variety of systems, allowing users to monitor and analyze communication.
3. Setting Up Antennas

Antennas form the backbone of your COMINT operation. Select the right antenna based on the frequencies you’re targeting. Higher frequencies require different types of antennas compared to lower frequencies. I struggled early on by using an antenna that wasn’t suited for my frequencies, which led to poor signal capture.
A key takeaway is to invest in high-quality, directional antennas. Aligning your antenna properly will also enhance your signal clarity. In certain cases, using multiple antennas for different frequency bands can make all the difference in signal reception. If you can afford it, consider getting specialized antennas for ELF-HF, as they are designed to cover long distances and penetrate various environments.
4. Software Configuration
Once your hardware is in place, configure your software to decode signals. COMINT systems are not only about hardware; software plays an equally crucial role. The software will decode the signals you capture, providing a comprehensive analysis of the communication. A standard software option like Krypto500 can decode a range of narrowband signals with ease.
As I transitioned to more complex systems, configuring the software became my focus. Always ensure your software is compatible with your hardware to avoid wasting time on technical issues. Regular software updates are also critical to staying on top of new developments and enhancements in the field.
5. Signal Processing and Data Storage

Signals must be processed efficiently, and data should be stored securely for later analysis. I often found myself overwhelmed by the sheer amount of data captured during sessions. To handle this, you will need robust data storage solutions with fast retrieval systems.
Start with a basic setup if you’re just monitoring a few signals, but scale up your storage options as the number of monitored frequencies increases. Some signals, especially those that span over days, can require significant storage space, and it’s better to over-prepare than be caught short.
6. Maintenance and Upgrades
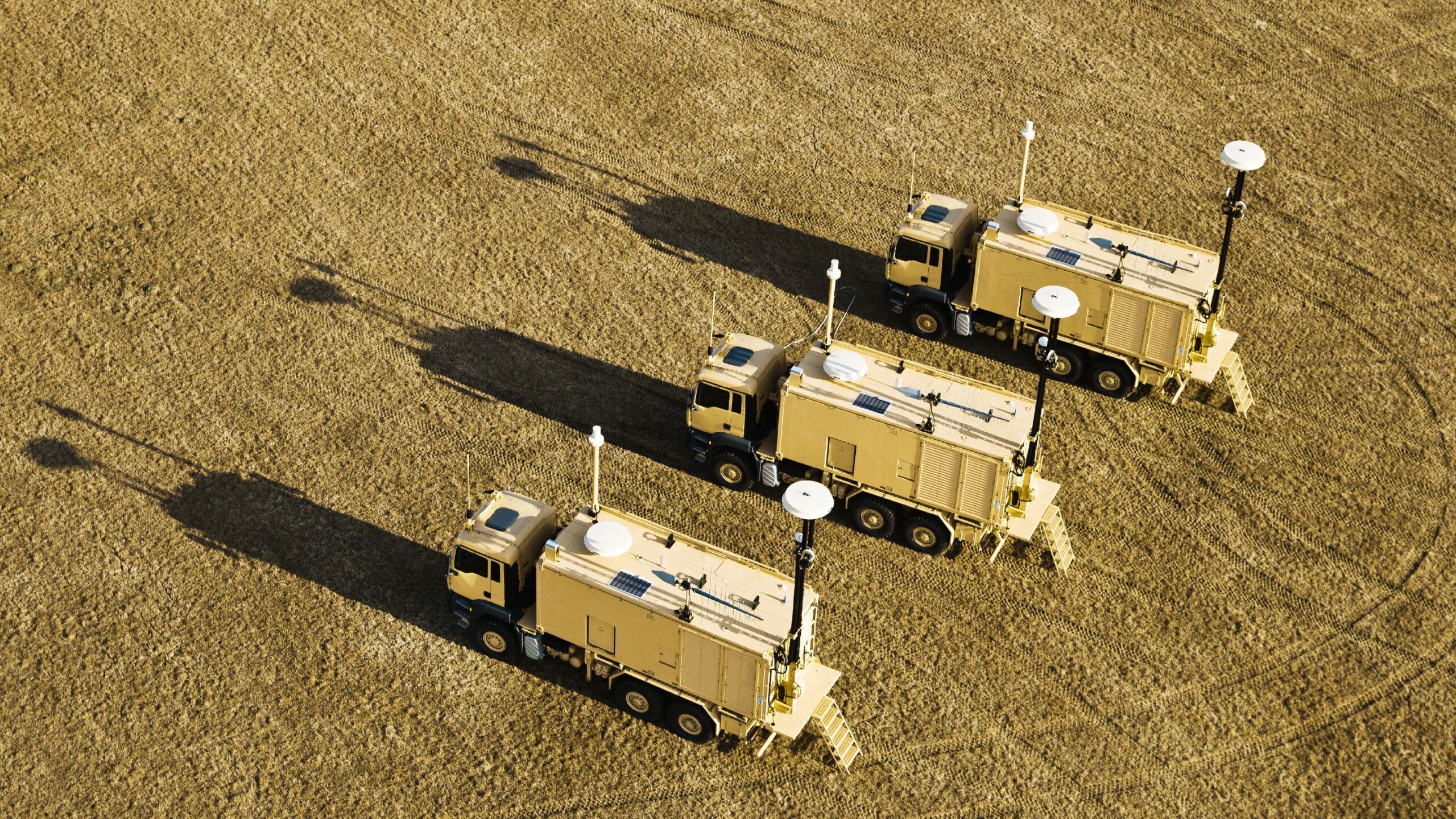

Dust and weather conditions can affect your antennas and receivers. In my experience, regular equipment checks and software updates are necessary to keep your system performing optimally. Never overlook the importance of firmware updates, as they can introduce new functionalities and improve signal decoding.
As you gain more experience, you will identify opportunities to upgrade. Whether it’s adding more advanced antennas or upgrading your storage capacity, always be proactive in keeping your system up-to-date.
Setting Up a COMINT System: A Simplified Checklist
| Step | Key Actions |
| 1. Define Scope | Identify the signals and frequencies to monitor. |
| 2. Choose Hardware | Select appropriate receivers, antennas, and decoders. |
| 3. Antenna Setup | Choose directional antennas based on frequency needs. |
| 4. Software Configuration | Install and configure compatible decoding software. |
| 5. Signal Processing & Storage | Ensure data is processed and stored securely. |
| 6. Maintenance | Conduct regular hardware and software maintenance. |
FAQ
1. Can a beginner set up a COMINT system?
Yes, with the right guidance, a beginner can set up a basic COMINT system, though more advanced setups require experience.
2. How much does setting up a COMINT system cost?
The cost depends on the complexity of the setup. Basic systems can be affordable, while advanced configurations can be more expensive.
3. What kind of maintenance is required?
Regular hardware checks and software updates are essential to ensure your COMINT system remains effective.
In conclusion, setting up a COMINT system can feel daunting at first, but it becomes manageable with the right approach. Begin by defining your scope, select the right equipment, and make sure your software and hardware are compatible. Don’t forget that antennas play a key role, and regular maintenance will extend the life and performance of your system. Above all, keep your objectives in mind and build a system that meets your needs efficiently.